From assistant to agent: The evolution of AI in M365
Table of contents
Back in 2005, your mobile phone suddenly started predicting the word before you finished it. At first, it was strange, but soon, you were flying through messages. Your Word doc began correcting the typos you made; the calculator would suggest functions, and slowly, quiet intelligence started making life easier.
Fast-forward to today, that same quiet intelligence has evolved into something way bigger: An agentic AI that doesn’t just assist but acts, thinks, and even predicts what you’ll need next.
The emergence of autonomous agents
Microsoft’s invention and integration of artificial intelligence (AI) started years ago, transitioning from simple assistance features to advanced agentic AI.
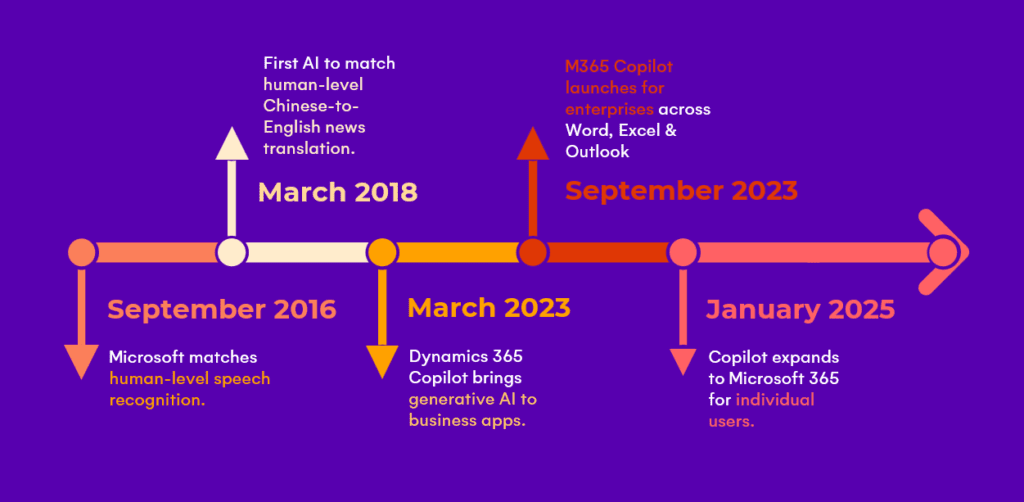
SOURCES: Microsoft 2016, Microsoft 2018, Microsoft March 2023, Microsoft September 2023, Microsoft January 2025
It started with predictive models that analyzed data using machine learning and anticipated final results. This was followed by generative AI, which introduced the ability to create text, images, and even music.
Now, we’re entering the era of agentic AI.
What is agentic AI?
Agentic AI is an advanced form of AI that doesn’t just respond to commands. It operates autonomously, completing tasks that were once only possible as the result of human effort. Those agents observe their environment, understand goals, and take actions with limited or no human supervision whatsoever.
AI agents aren’t just tools anymore. They represent a leap from simple assistance to independent decision-making.
How does agentic AI differ from traditional AI?
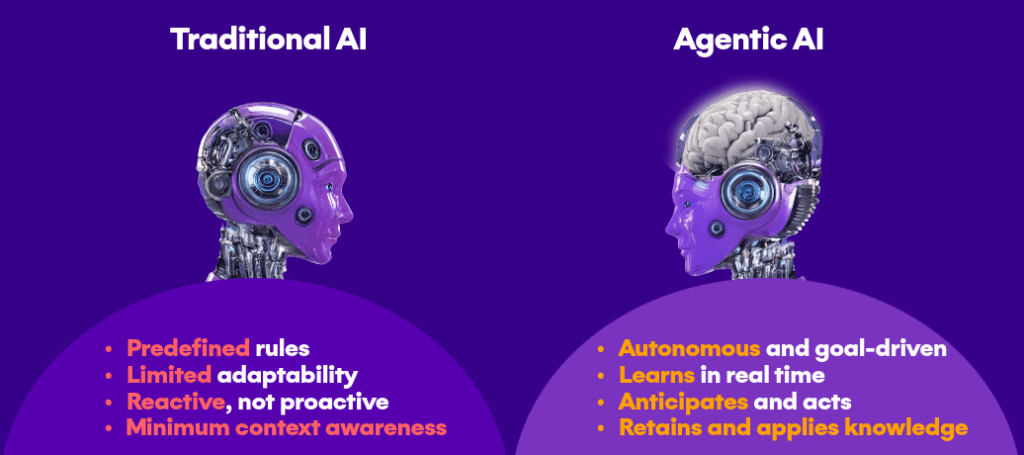
Unlike AI assistants that rely on human prompts, AI agents can assess situations, learn, and take initiative to achieve specific goals.
While traditional AI provides insights, executes commands, or automates set tasks, agentic AI is designed to adapt to new situations, adjust to changes, and work proactively.
How does agentic AI work?
To fully understand how agentic AI work, let’s explain how agentic AI differs from traditional AI in decision-making.
Traditional AI systems follow a clear input-output pattern. You give them a command (input), they analyze it and return a result (output). The logic behind this is often based on if-else conditions, pre-trained models, or automation scripts.
Traditional AI example:
A chatbot assistant that answers IT-related questions:
- You type: “How do I reset my password?”
- The AI searches a knowledge base and retrieves a predefined response.
- If it doesn’t know the answer, it asks you to clarify or transfers you to a human.
The key takeaway? Traditional AI only responds to prompts and follows a script.
Agentic AI example:
Now, imagine an AI agent managing M365 security settings. Instead of waiting for an admin’s request, it:
- Monitors permission changes in real time.
- Detects unusual access patterns.
- Decides whether to restrict access or alert IT.
- Acts automatically by revoking risky permissions or flagging them for review.
This is the difference: agentic AI doesn’t wait for instructions. It takes action.
What are some real-world applications of agentic AI?
The adoption of AI is accelerating at a remarkable pace among both businesses and individuals. It stands at 39.4%, outpacing the early growth of past technologies like personal computers and the internet.
For comparison, three years after PCs became widely available, their adoption rate was just 20%, similar to the internet’s rate two years post-launch.
While AI adoption in organizations hovered around 50% for several years, McKinsey & Company’s 2024 survey reveals a sharp increase, with adoption rising to 72%.
Here are a few real-world agentic AI use cases:
Project & collaboration management
- AI-powered meeting insights: Agentic AI can transcribe conversations, summarize discussions, and even provide follow-up actions in Microsoft Teams.
- Intelligent task management: AI algorithms can predict how long it will take someone to accomplish specific tasks, prioritize them, organize schedules based on more involved project scopes, set up calendars, notify stakeholders, and even suggest optimal time slots for different tasks.
- AI-based data insights for decision-making: AI can be used in big data analytics to extract meaningful insights from large data sets and automate decision-making processes. In 2025, Gartner predicts that 95% of decisions that currently use data will be at least partially automated.
IT & security
- Automated document sharing: Organizations use AI to simplify and automate document sharing across Teams and SharePoint.
- AI-driven chatbots for IT support: They can instantly resolve common issues like password resets, escalate complex problems to human agents, and reduce costs while improving efficiency.
- Smart email filtering: Companies are using advanced AI algorithms to identify spam and phishing attempts.
IT Operations & governance
- Predictive maintenance for IT systems: Organizations rely on AI to predict equipment failures before they happen, ensuring proactive maintenance rather than reactive repairs.
- Automated user provisioning: Companies use AI agents for user onboarding by automatically assigning permissions based on roles.
- Resource optimization using AI: Many organizations rely on agentic AI to analyze historical and real-time usage patterns to predict future resource demands, ensuring that computing power, storage, and network capacity are allocated efficiently.
Challenges of unsupervised agentic AI use
However, as attractive as autonomous agents in enterprise environments are, they bring considerable challenges, differing from the organization’s structure, regulations, and AI use cases.
So, let’s examine agentic AI use cases more closely, considering unexpected security and compliance gaps that could emerge if left unchecked.
Project & collaboration management
- AI-powered meeting insights: While this is an exciting feature for a broader user scope, without proper data governance, sensitive discussions may be recorded, which leads to potential breaches of confidentiality.
- Intelligent task management: Businesses using agentic AI for project management often find that AI agents lack the full business context humans naturally bring to decision-making. In real business scenarios, subtle factors like company strategy, recent events, unwritten constraints, etc., exist that an AI agent simply cannot consider.
- AI-based data insights for decision-making: Agentic AI lacks human intuition and context, which means it might misinterpret key details, such as prioritizing cost savings, leading to decisions that don’t align with business goals.
IT & security
- Automated document sharing: Without proper governance, agentic AI can give users broader access than they have the right to, making it easy for sensitive documents to end up in the wrong hands.
- Smart email filtering: While effective, there are cases where sophisticated phishing attempts slip through, especially as attackers evolve their tactics. Microsoft has acknowledged challenges in keeping up with increasingly sophisticated phishing methods, underscoring the need for ongoing vigilance and additional security layers.
IT Operations & governance
- Predictive maintenance for IT systems: Relying too much on agentic AI without human oversight can result in missed security patches or misconfigured servers – small oversights that could escalate into costly downtime.
- Automated user provisioning: If agentic AI misjudges user needs, it can assign too many or too few licenses, wasting budget on unused seats or leaving employees without essential access.
Governance as a standard pillar
Autonomous agents are a game-changer. However, organizations need strong governance to keep it in check.
In data governance, well-structured policies answer fundamental questions like who can see the data, for what cause, and under which conditions.
For agentic AI, the same principles apply:
- Defined purpose: What specific tasks or objectives is the AI agent designed to handle?
- Access control: Which data, systems, or tools can it interact with, and how is that access managed?
- Oversight & escalation: When does the AI agent require human intervention, additional approval, or restrictions?
- Performance & compliance monitoring: How do organizations measure effectiveness and stay within compliance guidelines?
- Ownership & accountability: If the AI agent makes an error or triggers a compliance risk, who is responsible for reviewing, correcting, and preventing future issues?
Agentic AI looking ahead
As AI in M365 shifts from reactive to proactive, two things are important: not to stall innovation and to stay in control. Because without proper oversight, AI agents can expose sensitive data, bypass compliance policies, and create security blind spots.
That’s where Syskit Point comes in.
With Syskit Point, AI agents operate under clear rules. There is no unchecked access and no security blind spots. It continuously monitors access, prevents data leaks, and ensures compliance.
Instead of wondering who has access to what or whether AI is making the right decisions, Syskit Point ensures only the right people see the right data at the right time, without the risk of accidental exposure.
AI agents might be smart, but on Syskit Point’s watch, they’ll play by the rules.
Try it today and keep your M365 environment in check.


